CUSTOMER SERVICE
Hotline : Mr. Bôn: 0938.788.646
Hotline :0909.219.889
Date 20/Jul/2016 at 07:41 AM

CHART OF THE PROCESS OF HANDLING
Using a septic tank and leach field underground to pretreatment waste water

Part design septic tank and leach field underground will be presented in detail in Waste Water Treatment II subjects.
The process for handling sewage or wastewater of industrial plants


Sewage
sludge or solids
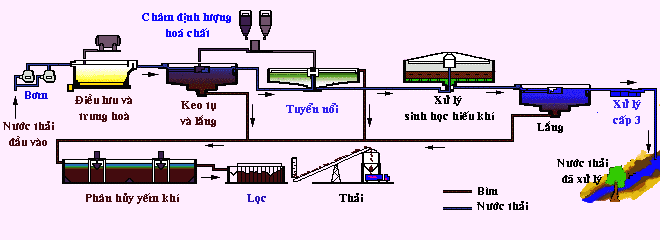
Note: The above are just some of the typical diagram, depending on the conditions we can install additional components or change the process.
The point to be noted in the design of treatment processes
1. The feasibility of the treatment process: the feasibility of the treatment process based on experience, data and publications about the research on the model and reality. If this is a completely new process or unusual factors, the study of patterns is essential.
2. Flow ranges can be applied. For example, wastewater stabilization ponds are not suitable for wastewater treatment with heavy traffic.
3. Able to withstand the volatility of the flow (if the fluctuations are too large to use the tank to save)
4. Characterization of waste water to be treated (for decision process chemical treatment or biological)
5. Substances in wastewater inhibitors for processing and can not be destroyed by the process.
6. Limitations due to climatic conditions: temperature especially as it affects the reaction rate of the process chemistry and biology.
7. The effectiveness of treatment systems: often indicated by the nature of the waste water output.
8. The following substances created as sludge treatment process, solids, water and gas are to be estimated on the number. Usually, people use the model to determine the section.
9. Sludge treatment: picking up the sludge treatment process at the same time with the selection process of wastewater treatment in order to avoid the difficulties that may occur subsequent to the disposal of sludge.
10. Environmental restrictions: prevailing wind direction during the year, near residential areas, graded water ... can be the limiting factor for the selection of treatment systems.
11. The need to use chemicals: sources and quantities, factors affecting the increase in the amount of chemicals used and the processing cost.
12. Energy use: its power and influence to the processing cost.
13. Manpower: including workers and technicians. Need training to some extent.
14. Operation and maintenance: the need to provide the conditions and special parts for the operation and maintenance.
15. The reliability of the processing system including the case of running overload or under load.
16. The complexity of the treatment system.
17. Compatibility with systems and equipment available.
18. The area of land used, including buffer areas for treatment systems.






